[C++] 구조체
판다코딩 C++ 인강 공부 정리
[ 전체 코드 ]
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main(){
//축구선수
struct MyStruct
{
string name;
string position;
int height;
int weight;
} B;
MyStruct A;
A.name = "Son";
A.position = "Striker";
A.height = 183;
A.weight = 77;
/*
MyStruct A = {
"Son",
"Striker",
183,
77
}
*/
cout << A.name << endl;
cout << A.position << endl;
cout << A.height << endl;
cout << A.weight << endl;
B = {
};
cout << B.height << endl;
/*
MyStruct A[2] = {
{"A", "A", 1, 1},
{"B", "B", 2, 2}
};
cout << A[0].height << endl;
*/
return 0;
}C++의 특장점은 사용자의 정의대로 원하는 데이터형을 만들 수 있는 것.
그 장점이 가장 잘드러나는 복합데이터형이 바로 구조체.
구조체 : 다른 데이터형이 허용되는 데이터의 집합
cf) 배열 : 같은 데이터형의 집합
struct로 구조체 선언 후 변수의 이름을 입력하고 구조체에 담기는 내용을 { } 중괄호로 묶어서 사용함.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main() {
struct MyStruct
{
string name;
string position;
int height;
int weight;
};
MyStruct A;
A.name = "Son";
A.position = "Striker";
A.height = 183;
A.weight = 77;
cout << A.name << endl;
cout << A.position << endl;
cout << A.height << endl;
cout << A.weight << endl;
return 0;
}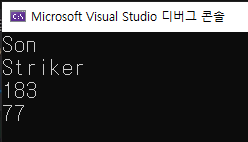
A라는 이름의 Mystruct형 변수를 선언한 것.
A는 Mystruct의 멤버(name, position, heght, weight)에 대한 정보를 담고있다.
멤버에 대한 정보를 담기위해서는 구조체의 멤버 연산자 .(dot)를 사용한다.만든 구조체 변수의 이름(A) 입력 후 .(dot)을 사용하면 멤버(name, position, heght, weight)에 접근할 수 있다.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main() {
struct MyStruct
{
string name;
string position;
int height;
int weight;
};
MyStruct A = {
"Son",
"Striker",
183,
77
};
cout << A.name << endl;
cout << A.position << endl;
cout << A.height << endl;
cout << A.weight << endl;
return 0;
}
구조체도 선언하면서 값을 대입하는 초기화의 방식 을 사용할 수 있다.
,(콤마)로 멤버들간의 값을 구분함.
,로 구분된 멤버들의 값은 각각 순서대로 멤버들에게 대입됨.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main() {
struct MyStruct
{
string name;
string position;
int height;
int weight;
} B;
B = {
};
cout << B.height << endl;
return 0;
}
중괄호 뒤에 사용할 변수명을 입력한다면 (B)
새로운 구조체를 선언하지 않아도 입력한 변수명으로써 구조체가 자동으로 만들어진다.
구조체 역시 배열처럼 값을 기입할 때 구조체의 멤버에 해당하는 모든 값을 기입하지 않아도 된다.
빈 중괄호로 선언을 하게 된다면 빈 값들은 각각 0에 해당되어 저장된다.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main(){
struct MyStruct
{
string name;
string position;
int height;
int weight;
};
MyStruct A[2] = {
{"A", "A", 1, 1},
{"B", "B", 2, 2}
};
cout << A[0].height << endl;
return 0;
}
구조체 역시 배열로 선언할 수 있다.
구조체로 사용할 이름을 명시하고 배열을 선언하듯이 [ ] 대괄호로 배열의 크기를 지정한다.구조체의 배열은 { } 첫번째 중괄호를 열고 그 안에 한번 더 { }를 사용하여 배열의 첫번째 인덱스에 해당하는 원소의 값을 넣고 ,(콤마)로 구분한다.
배열에 관련하여 각각 원소들의 멤버에 접근하는 방법A(구조체 이름) + [0](중괄호, 인덱스번호) + .(멤버연산자) + 멤버 이름